Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12:- Enhancement of the food production has become a necessity with ever-growing demand for the food supply due to population explosion. Application of the biological principles to the plant breeding and animal husbandry plays a major role in the boosting of human efforts to increase the crop production.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 Introduction
Furthermore, in promoting the food production, numerous new techniques such as the tissue culture techniques and the embryo transfer (Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer) are being developed and being practised. Where the plant breeding can be used to create the varieties that are resistant to the pathogens, thereby increasing yield of the crops, animal husbandry, on other hand, ensures to cater to needs of the food from the animals and the plant products by taking care of animals and breeding domestic animals through application of the scientific principles.
Given below are few questions on the Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Class 12. The explanations are also provided for the reference.

Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 – Very Short Answer Types Questions-
Q.1. Why were the millions of chickens killed in Assam, West Bengal, Maharashtra and Orissa in the recent years?
A.1. It was due to the diseases- Bird flu.
Q.2. Can the gamma rays be used in the crop improvement programmes?
A.2. The analysis of the plants is carried out in the closed chambers. These plants are consequently being tested for the desired mutations to be induced to breed further. The irradiated plants do not possess any adverse effect of the radiation, hence are not harmful and can be used.
Q.3. Why does mating of the two closely related animals after a few generations lead to the loss of the fertility and vigour in the animal husbandry?
A.3. Since the recessive alleles tend to get together and express causing harmful effects in progeny.
Q.4. Where and how is a man-made cereal being developed? Write one example.
A.4. The example is Triticale.
It is developed by a cross of plants – common wheat (Trilicumaestivum) and the European rye (Secalecereale). It is used as a substitute to the wheat in a few parts of world.
Q.5. Fill up:
A.5.
Fill up –
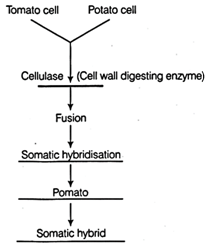
Q.6. What do you mean by hidden hunger?
A.6. Hidden hunger is consumption of the food that lacks in the nutrients specifically, micronutrients like the vitamins and the proteins.
Q.7. Why do the plants derived from the protoplast culture are named as the somatic hybrids?
A.7. Since it is formed after fusion of the two different varieties of the isolated protoplasts, where each possesses a desirable character to obtain the hybrid protoplast which can further be grown to form the plant.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 Quiz
Q.8. What do you mean by protoplast fusion?
A.8. It is ability of the protoplasts to form a hybrid protoplast that is obtained from the two different cells that fuses.
Q.9. Explain why the culture meristems are easier to be cultured compared to the permanent tissues?
A.9. Meristems divides continuously which is facilitated by the thin and the elastic walls thus suitable for the tissue culture as opposed to the permanent cells which have to differentiate to divide and possess the thick walls.
Q.10. Why are the proteins being synthesized from the single cell proteins, Spirulina?
A.10. The single celled proteins are the proteins produced by the microorganisms. One such unicellular microbe is Spirulina. Thus, proteins produced by the Spirulina is termed as the single-celled protein.
Q.11. What do u mean by aquaculture? Write the name of an animal that can be multiplied by the process of aquaculture.
A.11. Aquaculture is the process of culturing of the plants and the animals in freshwater. For examples – Shrimps, Oysters, and Shellfish etc.
Q.12. Explain the role of a veterinary doctor in management of the poultry farm.
A.12. The veterinary doctor ensures safe and proper farm conditions to keep the animals free from the diseases and treats them in case they pick up a disease.
Q.13. Can the plants obtained from the micro-propagation be referred to as ‘clones’?
A.13. Yes, as they are genetically identical to each other and parent plant,and hence called as the clones.
Q.14. Write the difference between a hybrid and a somatic hybrid.
A.14. A hybrid is obtained by the crossing of two selected plants of the opposite sex whereas , somatic hybrids are obtained by uniting any protoplasts from the two different varieties of the plants which are further cultured.
Q.15. What do you mean by emasculation? When it is done and why? Explain.
A.15. Emasculation is the removal of the stamens from bisexual flower that is used as a female parent in the process of plant hybridization. It is done so as to avoid the unwanted self-pollination. It is to be done at the bud before anthers dehisce.
Q.16. Write the two main limitations of plant hybridization programme?
A.16. The following are the limitations:
1.Compatibility of the parents.
2.Limited availability of the identified disease-resistant genes in the crops.
3.It is a tedious and very time-consuming process.
Q.17. Why intergeneric crosses are almost unknown and interspecific crosses rare in the nature?
A.17. Male and the female animals of the two varied related species are mated in the interspecific crosses and their fertility varies.
In a certain case, progeny may display desirable features of both parents and may be of economic value.
Example – A mule, whereas female counterparts can breed with species which is rare in nature. The Intergeneric hybridization, on other hand, is cross of the two different genera which is almost unknown in nature. They never forms complete zygote and are infertile.
Q.18. Write a difference between the aquaculture and the pisciculture.
A.18. Pisciculture is fish farming done in the isolated water bodies whereas the culturing of the aquatic animals and the plants in the freshwater is known as aquaculture.
Q.19. Justify the term ‘desirable trait’ with suitable the examples.
A.19. The desirable trait can be different for the different plants.
The listed are traits incorporated:
The higher the tolerance levels in response to environmental stress – bajra, maize, jowar are resistant to water stress.
Pathogen-resistant – Moong bean is resistant to the powdery mildew and the yellow mosaic virus.
Improved crop quality and the high-yield – Atlas 66 utilized as a donor to develop the wheat varieties with the enhanced protein content.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12
Q.20. What do you mean by Biofortification? How many methods you know for Biofortification?
A.20. The process of producing new and improved quality of the crops are known as the Biofortification.
There are the methodology of the Biofortification involves the two principle methods –
1.Selective breeding.
2.Genetic modification.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 – Short Answer Types Questions
Q.1. Through example of H5N1 virus, explain how the diseases are fast spreading due to the globalization and increased movement of the people.
A.1. Bird flu is a recent and the significant issue which involves aspect of global health.
The influenza-A virus(H5N1) is mainly observed in the birds and is contagious. It can be fatal and advances due to increasing the integration of countries i.e., globalization. It facilitates virus to travel to the places without the impediment. Once acquired by the human beings, it spreads across at a faster pace with the afflicted people travelling, especially through the air travel. In this way it spreads throughout.
Q.2. What do you mean by blue revolution?
A.2. Blue revolution refers to refers to the noticeable emergence of the aquaculture as a significant and highly productive agricultural activity.
Q.3. Explain why and how does the beehive help in enhancing yield?
A.3. When cultivated in fields of Brassica, apple, pear and the sunflower. Beehives causes an increase in pollination efficiency of the flowering plants and hence improves yield.
Q.4. Write the name of the method which can be used to deal with both the malnutrition and the lifestyle diseases.
A.4. Biofortification can be used to address both the issues. It focuses on improving quality of the food with through good quality – oil, protein, vitamin, micronutrient and mineral content. These oils are required to be rich in omega three fatty acids which are good for human heart. Proteins are required to have the essential amino acids,AA, such as tryptophan and lysine.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12
Q.5. In the animal husbandry programmes, how can success rate of the fertilization during the artificial insemination be improved?
A.5. Through the Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer(MOET) program, a cow is administered with the hormonal treatment so as to produce more than one ovule per cycle. In post artificial insemination, embryos at 8-32 celled state are then transported to the surrogate mothers.
Q.6. Explain germplasm collection. Write its advantages?
A.6. Germplasm is collection of all the diverse alleles of all genes of a crop plant. It offers following:
It provides entire alleles and the genes to the breeders and also characteristics which a plant expresses.
Most favourable characters of a specific gene are selected by breeder to manipulate it and transfer to desired parent.
Q.7. Which characteristic of the wheat helped India to attain green revolution?
A.7. Improved characteristics are as follows:
1.High-yielding attributes.
2. Speedy yielding feature.
3.Semi-dwarf nature.
4.Resistant to the diseases.
Q.8. What features of plants can help to resist the pest and the insect infestation?
A.8. The features are as follows –
1.Rendering flowers are nectarless.
2.On the aerial parts of the plants, increasing hair growth.
3.Facilitates the plants to produce the insect-killing chemicals.
Q.9. Why is it easier to culture plant cells in vitro as compared to animal cells?
A.9. It is because plant cells have the ability to grow into a new plant and are termed as totipotency and are limited in case of animals.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12
Q.10. Why is the culture medium referred to as highly enriched lab soil?
A.10. It is a highly enriched laboratory soil as they provide the carbon sources such as the sucrose, vitamins, inorganic salts, amino acids and the cytokinins and auxins(growth regulators) for plant to grow.
Q.11. Do the de-differentiation and a higher degree of the success attained in the plant tissue culture experiment related to each other?
A.11. Yes, they both are related to each other. Plant tissue culture can be more successful as any tissue can be produced even from the differentiated cells whereas when the cell dedifferentiates once, it gets regressed back to its embryonic stage where from it can again differentiate into any form of the tissue.
Q.12. Differentiate between a breed and a species by giving an example.
A.12. Species is building block of the biological classification and a taxonomic rank. It is a collection of a large group of the entities that are capable of interbreeding and producing the fertile offsprings.
For example – Cow and dog.
A breed is a specific group of the plants or the animals that have homogenous behaviour, appearance and other characteristics which help in distinguishing the plants and the animals of same species. For example – American Bulldog, Afghan Shephard.
Q.13. What is the utility of the plants that are raised through the clones of parent plant?
A.13. Plants that are raised through the tissue culture are useful as they are identical copies of parent plant and helps in maintenance of desired traits of parent plant.
Q.14. Write the significance of the testing new plant varieties in a country like India.
A.14. Testing is carried out on the farmer’s field for three growing seasons at least at the different locations across all agro-climatic zones where the crops are usually cultivated. Material is assessed in the comparison to best local crop cultivator available which is called as a reference or a check cultivator.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12
Q.15. What is ‘stress’ in plants? What are the types of stress in plants?
A.15. It can be defined as the external factors that negatively influence the plant productivity, growth, survival and the reproductive capacity. These factors can be broadly classified into:
Biotic or the biological stress factors
Environmental stress or abiotic factors – drought, and temperature etc.
Q.16. What do u mean by natural selection and the artificial selection? How does the artificial selection influences evolution process?
A.16. The natural selection is a key mechanism in the evolution process and is a non-random, gradual process in which biological traits become common in a population as a function of the distinct characteristic, which acts as a sieve through which a few variations can pass. In the process of artificial selection, plants and animals with desirable traits are considered and favoured for reproduction. Also called as selective weeding, it promotes the traits suiting the human preferences.
Q.17. How are the pure lines created in the animal husbandry?
A.17. Inbreeding of the 4-6 generations is essential to evolve the pure line in any animal. It aids in accumulation of the superior genes and helps to eliminate less desirable genes by promoting the homozygosity.
Q.18. In protoplast fusion experiment, name physical barriers of a cell. How to overcome barriers?
A.18. In this experiment, cell wall is most significant physical barrier. It can be overcome by treating it with the pectinase and the cellulase enzymes that have potential to digest cell wall and release bare protoplast girdled by cell membrane only.
Q.19. Write a few examples of the biofortified crops. How do they benefit the society?
A.19. Some of the examples are – Wheat, rice, bathua spinach, maize, and pulses Benefits for the following are –
-Fortified wheat is high in protein content.
-Maize hybrids have twice amount of the amino acids.
-Fortified rice has high levels of the iron.
-Consumption of the biofortified food improves the public health.
-If 2 or 3 nutrients are incorporated into a single crop it would benefit the consumers to overcome the nutrient deficiencies prevailing.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12
Q.20. Write the difference between the inbreeding and the outbreeding animals?
A.20. Inbreeding refers to the mating with the individuals of the same species. Outbreeding refers to the mating between the individuals of the different species.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12 – Long Answer Types Questions
Q.1. What are various steps that a Botanist will undertake to release a new variety of the plant?
A.1. The following are the steps:
Collection of the variability – Genetic variability is root of any breeding programme. Preservation and the collection of the various wild varieties of the species and the variants of cultivated species is a primary source for the productive exploitation of the natural genes in a population. It has germplasm collection.
Selection and the Evaluation of parents – Germplasm is assessed to identify the plants with the desirable traits. The selected plants thus obtained are multiplied and utilized in process of the hybridization. Wherever possible, pure lines are being created.
Cross-hybridization: Desired characters from the selected parents are often combined from the two different parents. It is a time consuming and a tedious process as the pollen grains from desired male plant have to the collect and placed on stigma of selected female plants.
Selection and the Testing of the Superior recombinants: Selecting the plants having the desired trait combination among the progeny. It is crucial for breeding objective and requires a scientific examination of progeny. It yields the plants that are superior to their parents, which are self-pollinated until they reach a state of uniformity so as to not segregate the characters in the progeny.
Testing, commercialization and the release of the new cultivators.
Q.2.
a)Why does a shift from the grain to meat diets create more demand for the cereals?
b) Write the name of this emerging area of the research where a 250kg cow produces 200g of the protein every day but 250g of the Methylophillus methylotrophus can produce 25 tonnes of the protein? State advantages of this area of the research.
A.2.
(a) Shift creates the demands for the cereals since it takes 3-10kg of the grains to produce 1kg of the meat through the animal farming.
(b) The name of research field is the single cell protein. As a source of the good protein, microbes is cultivated on a larger scale. For the instance, microbes like the Spirulina can easily be grown on the wastewater from the starch processing plants like the molasses, potatoes, animal manure and sewage to generate it in larger quantities which can be served as the food rich in micronutrients. It also reduces the environmental pollution.
Q.3. In the crop improvement programmes, how are the tissue culture methods beneficial over conventional methods of plant breeding?
A.3. The tissue culture was developed as conventional breeding method failed to keep the pace with demand and to provide the fast and efficient systems for crop improvement sufficiently. Advantages of the tissue culture are as follows:
Produces a large number of the plantlets by the micropropagation within a short period of time.
All the cells have a similar genotype and constitute a clone as they are derived from a single explant by the mitotic division.
By providing the salts, toxins etc tolerance to stress can be obtained in the culture medium in increasing the dosage. The surviving cells are then selected to raise the resistance in plants.
Through the meristem culture, virus-free plantlets can be obtained.
From the new plants, embryos which do not survive inside the seeds can be cultivated by the tissue culture.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12
Q.4.
a) How are mutations beneficial for plant breeding? Discuss with an example.
b) Explain in brief the technology that made us self-sufficient in food production.
A.4.
a) Through use of the radiations (gamma radiations) and the chemicals, it is possible to induce the mutations artificially in the plants. These plants are then selected and used to have the desired characteristics as a source of the breeding, which is referred to as mutation breeding. For the instance, in moong bean, resistance to the yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew was induced through the mutations.
b) Traditional farming yields the limited biomass for the animals and the humans hence better management practices can cause an increase in yield to a limited extent. As a technology, the plant breeding helps to increase the production to a large extent as it is significant in manipulation of the plant species to create the desired plant types suited for the cultivation with outcomes such as the better yields and disease-resistant plants. This technology also supports green revolution.
Q.5. How is plant cell totipotency being used for plant propagation and improvement?
A.5. It can be utilized by following measures:
It is possible to attain the propagation of the many plants in shorter durations with application of these methods. Banana, tomato, apple etc are produced on a commercial scale.
Through the micropropagation, it is possible to recover the healthy plants from the diseased plants which are done by extracting the meristems that are disease-free and growing it invitro which is done in the potato, sugarcane etc.
Q.6. Explain process of the somatic hybridization.
A.6. It takes place in following steps:
Fusion of the Protoplast: The isolated protoplast is devoid of the protoplast. Thus there are no barriers for the protoplast fusion. This can be achieved by the mechanical, induced or spontaneous fusion methods.
Hybrid Selection: After the protoplast fusion, a heterogenous mixture of the unfused chloroplast, homokaryons and heterokaryons are obtained. These hybrid cells (heterokaryons) are then selected through the biochemical, cytometric and visual methods.
Identification of the Hybrid Cells: The somatic hybrids are identified by the various molecular techniques such as the RFLP, AFLP, PCR, etc.
Click here to join our telegram channel for more questions and answers like Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Class 12



















